Having a baby is a beautiful but challenging adventure that takes a lot of energy and time off your schedule, so getting pregnant right away may not be in your plan list
In this article, we will tell you about ways that you can avoid getting pregnant right away without interfering with the process of breastfeeding; and if you are planning to have another child soon, or if you want the breastfeed to continue for a longer time and you are worry that it will overlap with your next pregnancy, we will tell you can do about it.
Always keep in mind that every person is different and that your doctor will have the best call regarding your specific case.
Can I get pregnant while breastfeeding?
During breastfeeding you can get pregnant, but your chances of doing so are lower.
Prolactin and oxytocin are the hormones that directly affect breastfeeding. When your baby breastfeeds, sensory impulses pass from your nipple to your brain which makes your body secrete prolactin and oxytocin.
Oxytocin is the hormone that plays a role in preventing you from getting pregnant right away, as one of the many functions of this hormone is to send signals to suppress ovulation, which means no pregnancy.
Some moms aren’t fertile for a few months during lactation because of oxytocin, which has been know to be a contraceptive method call:
The lactational amenorrhoea method (LAM) which is a period of time in which the menstruation hasn’t returned and the baby (less than 6 months old) is exclusively and frequently breastfed (this makes the mom to reduce the estrogen levels which makes menstruation not to show up).
*In order for LAM to work it is important to maintain breastfeeding constantly and exclusively, this means to avoid pacifiers, bottles or pumping manually and that your baby is still waking in the night to nurse.
Can I breastfeed while pregnant with another baby?
It is possible for you to breastfeed while pregnant with another baby, although there are some concerns or impacts that have been made about this.
The concern about breastfeeding while pregnant has to do with the hormone oxytocin; which is released while breastfeeding and is also responsible for contractions, so you may have contractions while breastfeeding. Some doctors may advise you not to breastfeed while pregnant because there is a small risk of preterm labor because of this.
Even so, there has not been found that healthy woman with a healthy pregnancy have a higher risk for miscarriage or preterm birth because of breastfeeding; so if you haven’t had miscarries, early deliveries and you have no complications during your pregnancy, your doctor may tell you that is ok for you to keep breastfeeding while pregnant.
There are some reasons (not safety related) that may make you stop breastfeeding while pregnant:
- The taste and volume of your milk may change during pregnancy which could make your baby wean because he/she may not like it anymore.
- your nipples may get sore, or you may have other effects that could cause you to feel tired or overwhelmed.
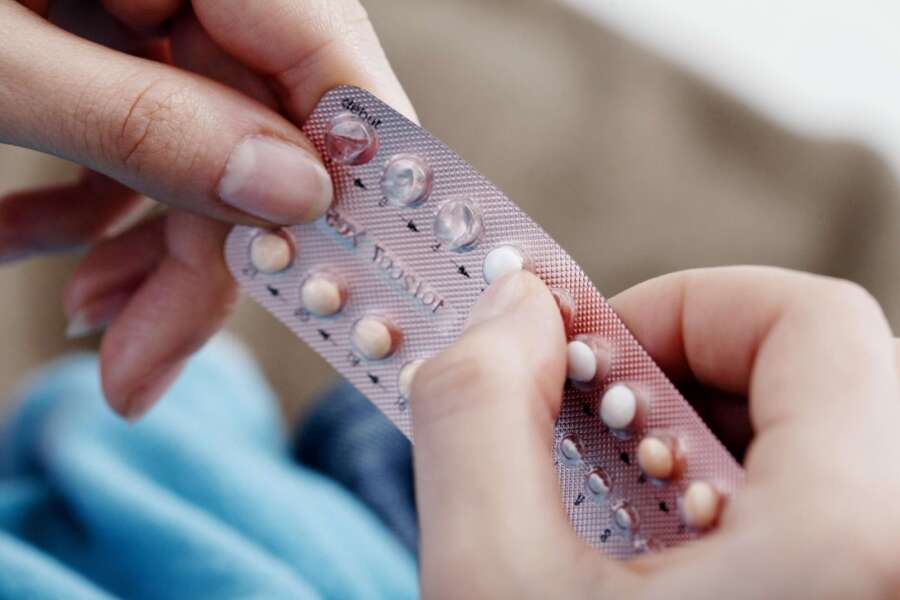
Can I take birth control while breastfeeding?
Even though your chances of getting pregnant while breastfeeding are lower than usual, if you are not planning to get pregnant at this time, it is important to use some birth control method ( even if it is LAM) because there is a possibility of getting pregnant.
What birth control is safe while breastfeeding?
Always keep your healthcare provider close to help you choose the right choice for you. In the following, we share with you some of the birth control methods that are known to be mostly safe while breastfeeding:
- LAM: As we mentioned before, if you are not ovulating, and you are exclusively and frequently breastfeeding, the lactational amenorrhea method may be a good choice for you for the first few months after delivery; but this isn’t the case for every mom.
- Mini-pill: is a progestin-only oral method. It is slightly less effective than the pills containing estrogen and progestin, but as your chances of getting pregnant are lower while breastfeeding, this may help while giving you less amount of hormones into your body.
- Progestin-only arm implants: Nexplanon, for example, is one of the most effective birth control options and can be inserted immediately after delivery.
- The Mirena IUD: which has a small amount of hormones that it releases in the uterus, and may not affect the quality and quantity of breast milk.
- Medroxyprogesterone (Depo Provera): is an injection that may not suppress milk production.
*Some women have a very strong reaction to even low dose hormonal methods. Keep in mind that by changing your hormone composition you have a chance of changing their balance which can have an impact on your supply. If you are in the use of any of these hormonal methods and you find changes in your feeding you may decide to stop using it in order to go back to your usual feeding.
Hormonal birth control effects
It is known that if a small amount of hormone passes into your breast milk it will not have bad effects on your baby, this is why progestin-only birth control is known to be safe during breastfeeding.
The contraceptives that include estrogen also, are only approved if low-dose when the breast milk production has been established as those can make some changes in your milk composition.
A small amount of hormonal birth control has even been found to have some good effects on the quantity and quality of breast milk; medroxyprogesterone (contraceptive injection) for example, may have an impact on the quality of fat concentration, calories, minerals and protein composition of breast milk.
Keep in mind that every case is different and not every birth control is good for everyone, ask your doctor which one would be best for your health and your lifestyle choices.
In Breastfeeding 101 we hope this information has been useful to you, and we love to invite you to follow all of our content to learn more about pregnancy, breastfeeding and your baby’s well being.
If you want to learn more about taking birth control while pregnant, we share with you some of the sources that made this article possible:
A Comparative Study of Breastfeeding During Pregnancy I JNR
Breastfeeding and Contraception: Why the Inverse Association? I JSTOR
Breast-feeding and fertility regulation: current knowledge and programme policy implications* I WHO
Breast‐feeding During Pregnancy and the Risk of Miscarriage I National Library of Medicine
Breastfeeding during pregnancy: position paper of the Italian Society of Perinatal Medicine and the Task Force on Breastfeeding, Ministry of Health, Italy I National Library of Medicine
Contraception During Breastfeeding I Cleveland Clinic
Effects of hormonal contraceptives on breast milk composition and infant growth. World Health Organization (WHO) Task Force on Oral Contraceptives I National Library of Medicine
Effects of maternal use of hormonal contraception during breastfeeding: Results from a British birth cohort I National Library of Medicine I ScienceDirect
Lactational amenorrhoea method for family planning I National Library of Medicine
Minipill (progesterone-only birth control pill) I Cleveland Clinic
Optimizing maternal and neonatal outcomes with postpartum contraception: impact on breastfeeding and birth spacing I National Library of Medicine
Progestogen-only contraceptive use among breastfeeding women: a systematic review I ScienceDirect
The physiological basis of breastfeeding I The National Library of Medicine
The Use of Breastfeeding as a Contraceptive I JOGNN
To Use or Not Use Combined Hormonal Oral Contraceptives During Lactation I JSTOR
Update to CDC’s U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2010: Revised Recommendations for the Use of Contraceptive Methods During the Postpartum Period I CDC
Annie Rueb






